Restorative practices are gaining recognition as effective strategies for creating a positive, inclusive, and collaborative learning environment. These practices focus on building strong relationships, fostering mutual respect, and addressing conflicts in a constructive manner. By implementing restorative practices in the classroom, educators can improve student behavior, enhance academic achievement, and create a more supportive and engaging educational experience. This guide explores how to effectively integrate restorative practices into your classroom setting.
1. Understanding Restorative Practices
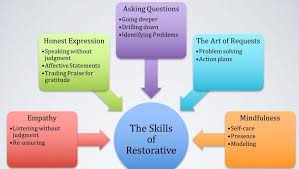
Before implementing restorative practices, it’s essential to understand their core principles and objectives.
1.1 What Are Restorative Practices?
Restorative practices are approaches designed to build community and manage conflict by emphasizing relationships and repairing harm rather than punishing wrongdoers. Key components include:
- Building Relationships: Fostering a sense of belonging and mutual respect among students.
- Addressing Harm: Focusing on the impact of behavior and working towards repairing relationships rather than simply punishing misconduct.
- Encouraging Accountability: Helping students understand the consequences of their actions and encouraging them to make amends.
1.2 Benefits of Restorative Practices
Implementing restorative practices in the classroom offers several benefits:
- Improved Student Behavior: Restorative practices help students understand the impact of their behavior and encourage them to take responsibility for their actions.
- Enhanced Classroom Climate: By fostering positive relationships and a sense of community, restorative practices contribute to a more supportive and collaborative learning environment.
- Reduced Discipline Issues: Schools that use restorative practices often see a decrease in disciplinary referrals and school suspensions.
2. Building a Restorative Classroom Culture
Creating a restorative classroom culture involves setting a foundation of trust, respect, and positive interactions.
2.1 Establishing Clear Expectations
- Create Classroom Agreements: Collaboratively develop classroom rules and agreements with students. This can help students feel involved in the process and understand the expectations for behavior.
- Model Positive Behavior: Demonstrate the behaviors and attitudes you expect from your students. Modeling respect, empathy, and effective communication sets a positive example.
2.2 Building Strong Relationships
- Get to Know Your Students: Take time to learn about your students’ backgrounds, interests, and needs. Building strong relationships helps create a supportive learning environment.
- Foster Open Communication: Encourage open and honest communication among students. Create opportunities for students to express their thoughts, feelings, and concerns in a safe and respectful manner.
3. Implementing Restorative Practices in Daily Interactions

Integrating restorative practices into daily classroom interactions helps reinforce positive behaviors and address conflicts effectively.
3.1 Restorative Circles
- Purpose and Structure: Restorative circles are structured discussions that provide a space for students to share their thoughts and feelings, discuss issues, and work towards resolution. Use circles to build community, address conflicts, or reflect on classroom experiences.
- Facilitating Circles: As a facilitator, guide the discussion with open-ended questions and ensure that everyone has an opportunity to speak. Use a talking piece to manage turns and promote respectful listening.
3.2 Restorative Conferencing
- Handling Conflicts: Restorative conferencing involves bringing together those affected by a conflict to discuss the impact of the behavior and work towards resolution. This process helps students understand different perspectives and collaboratively develop solutions.
- Steps in Conferencing: Begin by explaining the purpose of the conference, allow each participant to share their perspective, and then work together to agree on how to repair the harm and prevent future issues.
4. Teaching Restorative Skills and Techniques
Equipping students with restorative skills helps them manage conflicts and build positive relationships.
4.1 Empathy and Communication Skills
- Empathy Training: Teach students how to recognize and understand others’ emotions. Activities like role-playing and discussing different perspectives can help build empathy.
- Effective Communication: Provide opportunities for students to practice active listening, expressing themselves clearly, and using “I” statements to communicate their feelings and needs.
4.2 Problem-Solving and Conflict Resolution
- Problem-Solving Strategies: Encourage students to identify problems, brainstorm solutions, and evaluate the potential outcomes. Use guided discussions and activities to develop these skills.
- Conflict Resolution Techniques: Teach students techniques for resolving conflicts peacefully, such as negotiating, compromising, and finding common ground.
5. Addressing Challenges and Overcoming Obstacles
Implementing restorative practices can present challenges, but addressing these issues proactively can lead to successful integration.
5.1 Resistance from Students or Staff
- Addressing Resistance: Some students or staff may resist restorative practices due to unfamiliarity or skepticism. Provide training and support to help them understand the benefits and importance of these practices.
- Building Buy-In: Involve students, parents, and staff in discussions about the goals and benefits of restorative practices. Share success stories and demonstrate how these practices improve classroom dynamics.
5.2 Maintaining Consistency
- Consistency in Implementation: Ensure that restorative practices are consistently applied throughout the school. This includes integrating them into school-wide policies and practices.
- Ongoing Professional Development: Provide ongoing training and support for educators to help them effectively implement and sustain restorative practices in their classrooms.
6. Measuring the Impact of Restorative Practices

Assessing the effectiveness of restorative practices helps determine their impact on classroom dynamics and student outcomes.
6.1 Collecting Data
- Behavioral Data: Track changes in student behavior, such as reductions in disciplinary referrals and improvements in classroom climate.
- Student and Staff Feedback: Gather feedback from students and staff regarding their experiences with restorative practices and their perceptions of the classroom environment.
6.2 Evaluating Success
- Reviewing Data: Analyze the data collected to evaluate the impact of restorative practices. Look for trends and patterns that indicate improvements or areas needing adjustment.
- Adjusting Practices: Based on the evaluation, make necessary adjustments to improve the implementation of restorative practices and address any identified challenges.
7. Conclusion
Implementing restorative practices in the classroom can transform the learning environment by fostering positive relationships, enhancing student behavior, and promoting a supportive community. By understanding the principles of restorative practices, building a restorative classroom culture, integrating these practices into daily interactions, teaching essential skills, addressing challenges, and measuring their impact, educators can create a more inclusive and effective learning experience.
Restorative practices offer a proactive and collaborative approach to education that benefits students, teachers, and the entire school community. Embracing these practices helps build a strong foundation for a positive and engaging educational experience, ultimately leading to better outcomes and a more harmonious classroom environment.


