In today’s educational landscape, passive learning methods—like merely reading textbooks or listening to lectures—are increasingly recognized as insufficient for achieving deep understanding and retention. Instead, active learning techniques are gaining prominence as powerful strategies for effective studying. This approach involves engaging with the material in a more dynamic and interactive manner, leading to better comprehension and memory. This guide will explore how to use active learning techniques to enhance your studying effectiveness.
What is Active Learning?

Active learning refers to a range of teaching and studying strategies that require students to actively engage with the material, rather than passively absorbing information. It emphasizes interaction, problem-solving, and critical thinking. By involving learners in their educational process, active learning fosters deeper understanding and long-term retention of information.
Benefits of Active Learning
- Improved Retention: Active learning techniques encourage deeper processing of information, which leads to better retention and recall.
- Enhanced Understanding: By engaging with the material, students are more likely to grasp complex concepts and see connections between ideas.
- Increased Engagement: Interactive methods make studying more engaging and enjoyable, reducing the likelihood of procrastination.
- Better Critical Thinking: Active learning promotes critical thinking skills as students analyze, evaluate, and apply knowledge.
Active Learning Techniques
Here are some effective active learning strategies you can incorporate into your study routine:
1. Summarization
Overview: Summarization involves writing brief summaries of the material you are studying. This can be done by creating outlines, bullet points, or brief paragraphs that capture the main ideas.
How to Use It:
- After Reading: Write a summary of each section or chapter after reading it. Focus on capturing key concepts and main arguments.
- During Study Sessions: Use summarization to condense notes into concise, manageable chunks that highlight the most important information.
Benefits: Summarization helps reinforce learning by forcing you to process and rephrase information in your own words.
2. Self-Explanation
Overview: Self-explanation involves explaining concepts or problems to yourself or others. This method helps clarify your understanding and identify gaps in your knowledge.
How to Use It:
- Teach Someone Else: Explain concepts to a peer or even to yourself out loud. Teaching requires you to articulate your understanding clearly.
- Use the Feynman Technique: Write down what you know about a topic as if you are teaching it to a child. Simplify complex ideas into understandable terms.
Benefits: Self-explanation promotes deeper understanding by forcing you to process information and connect it with what you already know.
3. Practice Testing
Overview: Practice testing involves regularly testing yourself on the material you are studying. This can be done through quizzes, flashcards, or practice problems.
How to Use It:
- Create Flashcards: Use flashcards to quiz yourself on key terms, definitions, and concepts.
- Take Practice Exams: Simulate exam conditions by taking practice tests. This helps you become familiar with the format and pressure of real exams.
Benefits: Practice testing reinforces learning and improves recall by creating retrieval cues that enhance memory.
4. Interleaved Practice
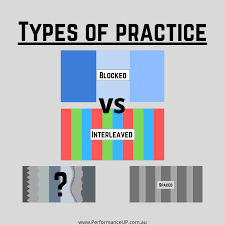
Overview: Interleaved practice involves mixing different topics or types of problems during your study sessions, rather than focusing on one subject at a time.
How to Use It:
- Mix Subjects: Alternate between studying different subjects or types of problems within a single study session.
- Varied Practice: Apply this technique to different types of problems or questions to improve your ability to transfer knowledge to new contexts.
Benefits: Interleaved practice helps improve problem-solving skills and enhances your ability to apply knowledge in various situations.
5. Collaborative Learning
Overview: Collaborative learning involves studying with others to discuss and solve problems together. This method leverages the diverse perspectives and knowledge of group members.
How to Use It:
- Study Groups: Join or form a study group where members can discuss and explain concepts to each other.
- Peer Teaching: Take turns teaching different topics to each other, which reinforces your own understanding.
Benefits: Collaborative learning provides social support, diverse perspectives, and opportunities for active engagement with the material.
6. Concept Mapping
Overview: Concept mapping involves creating visual diagrams that represent the relationships between concepts. This technique helps you organize and integrate information.
How to Use It:
- Create Diagrams: Draw concept maps that link related ideas and concepts. Use shapes and arrows to illustrate connections.
- Update Maps: Revise and expand your concept maps as you learn more about the topic.
Benefits: Concept mapping helps you visualize the structure of knowledge and see how different concepts relate to each other.
7. Real-World Application
Overview: Applying what you have learned to real-world scenarios helps deepen your understanding and see the relevance of the material.
How to Use It:
- Case Studies: Analyze case studies or real-life examples related to the subject matter.
- Projects: Work on projects or practical tasks that require you to apply the concepts you’ve studied.
Benefits: Real-world application reinforces learning by showing how theoretical concepts are used in practice.
Incorporating Active Learning into Your Routine
To make active learning a regular part of your study routine, consider the following tips:
- Set Goals: Define specific learning goals and objectives for each study session. This helps you stay focused and measure progress.
- Create a Study Schedule: Allocate time for different active learning techniques. Mix and match methods to keep your study sessions engaging.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly assess your understanding and adjust your study methods as needed. Reflect on what techniques work best for you.
- Stay Consistent: Consistent use of active learning techniques will yield the best results. Make active learning a habitual part of your study routine.
Conclusion
Active learning is a powerful approach to studying that can significantly enhance your understanding, retention, and overall academic performance. By incorporating techniques such as summarization, self-explanation, practice testing, and collaborative learning into your study routine, you can make your study sessions more effective and engaging. Embrace these strategies in 2024 to achieve better learning outcomes and develop a deeper connection with the material you are studying.


